Charming particle has a record-breaking lifetime
When quarks come together to form composite particles known as hadrons, they’re typically trios or quark–antiquark pairs. Although the possibility of more complex structures was hypothesized in the 1970s, it took about 30 years to find the first confirmed particle with four quarks. In the intervening years, researchers have observed nearly two dozen so-called tetraquarks and even several pentaquarks (see the Quick Study by Steve Olsen, Physics Today, September 2014, page 56
Daniel Dominguez/CERN
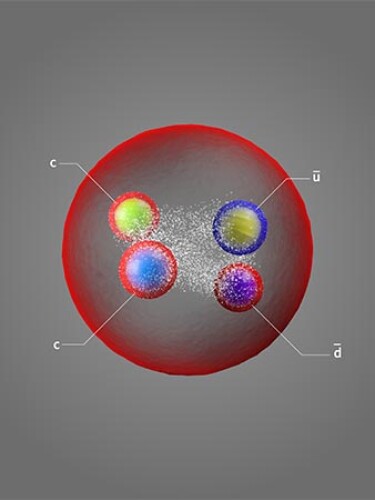
Quantum chromodynamics readily predicts the behaviors of high-energy particles, but at the lower energies found for quarks in hadrons, it struggles. At those energies, experiments, in particular on exotic particles, are a better guide. Now the Large Hadron Collider beauty (LHCb) collaboration has identified a new tetraquark with an impressively long lifetime. The tetraquark—composed of two charm quarks, an up antiquark, and a down antiquark—is promising for future research and hints at the existence of a similar particle of even greater interest.
For the data set of proton–proton collisions at the LHC between 2011 and 2018, the LHCb collaboration found a sharp peak in the mass spectrum of events with two D0 mesons and a π+ meson, the decay products of the proposed tetraquark. The peak corresponds to a particle mass of about 3875 MeV and falls just below the value for the summed masses of a D0 meson, which comprises a charm quark and an up antiquark, and a D*+ meson, which comprises a charm quark and a down antiquark.
The signal isn’t noise or chance—the statistical significance is more than 22 standard deviations. And the lifetime, as determined from the inverse of the peak’s width, is the longest of the tetraquarks found thus far. Most decay in just 10−23 seconds, a lifetime the new tetraquark outlasts by two orders of magnitude. A longer lifetime and corresponding narrower signal peak make detecting the particle’s properties easier and more accurate.
The four quarks could take two different structures: together in a single compact cluster or in two separated lobes, akin to a diatomic molecule but made of a D0 and a D*+ meson. So far, the LHCb results aren’t conclusive but suggest a molecule-type structure.
Values for the tetraquark’s quantum numbers are among the next tasks for the collaboration. The researchers also hope, inspired by their result, that they might find a tetraquark in which the charm quarks are replaced with two beauty quarks. The beauty version of the tetraquark is predicted to be stable with respect to the strong interaction, so its decay would happen even more slowly through the weak interaction. (R. Aaij et al., LHCb collaboration, Nat. Phys. 18, 751, 2022



